ABA therapy, or Applied Behavior Analysis, is a proven and structured approach used to help children with autism develop meaningful life skills. It focuses on improving behaviors that impact daily life—like communication, following instructions, and social interaction.
Through individualized ABA programs, children work on specific goals using data-driven strategies, with therapy tailored to their unique strengths and challenges.
In this guide, you’ll learn what ABA therapy is, how it works, what happens in a session, and how it supports children across different settings. We’ll also explore the benefits, address common questions, and explain how families play a key role in the process.
What Is ABA Therapy?
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), commonly known as ABA therapy, is a science-based approach that focuses on improving meaningful behaviors—such as communication, social skills, and daily routines. This method is especially effective for children with autism, but it also supports individuals with ADHD, developmental delays, and other behavioral challenges.
Applied Behavior Analysis works by analyzing how a person’s behavior is influenced by their environment. From there, therapists create a customized ABA program using proven techniques to teach positive behaviors and reduce those that interfere with learning or daily life. Many programs use structured tools like discrete trial training (DTT) to break skills into small, achievable steps.
What sets ABA apart from other therapies is its precision and adaptability. It relies on ongoing data collection, structured intervention, and measurable goals—not guesswork. While other therapies may take a more general approach, behavioral intervention is built around clear objectives and personalized strategies, often delivered over multiple hours a week for maximum impact.
How ABA Therapy Works
ABA therapy aims to improve behavior by examining the connection between actions and the environment. Therapists use observation and data to create personalized plans that help children build new skills and reduce behaviors that interfere with daily life.
Rooted in Science
This behavioral approach is not a guessing game—it’s grounded in scientific principles and ongoing evaluation. Practitioners collect data during each session and use it to adjust strategies in real time. If progress slows, they introduce other proven methods to keep the child moving forward.
According to the National Autism Center, ABA is the most effective therapy for children with autism, with up to 80% showing major improvements in communication and social skills.
One reason ABA is so successful is its flexibility. Therapists personalize interventions to fit each child’s unique needs. For example, if a child shows disruptive behaviors like hitting or biting, the therapist creates a plan to reduce those behaviors while teaching and reinforcing more appropriate alternatives.
Research-Based
ABA is one of the most researched therapies available. Its strategies are based on decades of studies showing success in building daily living skills and reducing challenging behaviors.
For parents seeking transparency in their child’s care, ABA stands out because its methods are backed by solid research. Studies published in The Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis highlight ABA’s role in increasing independence and social engagement in children.
Parents are encouraged to ask questions and review the research behind their child’s treatment plan. This ensures the approach aligns with proven strategies for long-term success. According to the Center for Autism and Related Disorders, early intervention with ABA leads to better outcomes, including stronger language skills and adaptive behaviors that support greater independence.
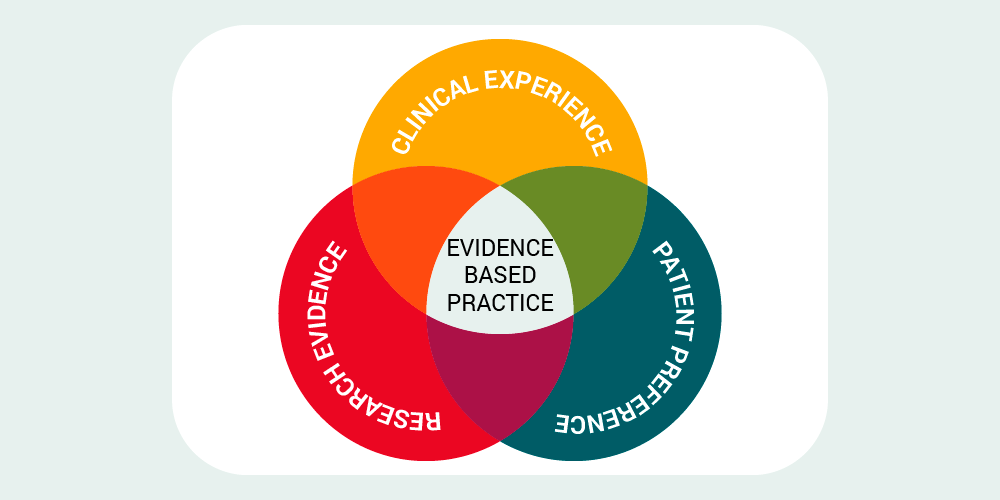
The Role of Data
A key feature of ABA therapy is its strong focus on data. Practitioners carefully track a child’s progress during each session, recording behaviors, responses, and skill development over time.
This data-driven approach helps therapists make informed decisions. If a strategy isn’t working, they adjust it based on real results—not guesswork. For example, a challenging behavior might make more sense once the therapist reviews what happens before and after it.
Data also tracks how well a child is learning new skills, such as communication, self-care, or social interaction. According to a study in The Behavior Analyst Today, ABA programs that use consistent data collection improve decision-making and treatment outcomes in 90% of cases.
Environmental Factors
One of the core strengths of this behavioral treatment is its attention to how a child’s environment affects behavior. Therapists don’t just observe the behavior itself—they also look at what happens right before and after it. This helps identify triggers and consequences that can be changed to support more positive behaviors.
For example, a child who struggles with transitions—like moving from playtime to nap time—might benefit from visual schedules, verbal cues, or timers. These tools can reduce anxiety and make transitions smoother.
By focusing on the environment, ABA therapy becomes not only effective but also practical. When surroundings are adjusted thoughtfully, children are better able to manage their behaviors at home, in school, and during social activities.
The Role of Board-Certified Behavior Analysts (BCBAs)
Board-Certified Behavior Analysts (BCBAs) play a vital role in delivering high-quality ABA therapy. These professionals receive extensive training and certification to design and oversee personalized treatment plans for each child.
BCBAs work closely with families to ensure therapy is aligned with the child’s unique needs and daily routines. This collaboration helps create consistency between sessions and real-life environments, which supports long-term progress.
In addition to planning interventions, BCBAs provide ongoing supervision and guidance to the therapy team. Their leadership ensures that all strategies meet high standards of care. Research shows that BCBA-supervised programs lead to stronger skill development and behavior improvements—especially in younger children.
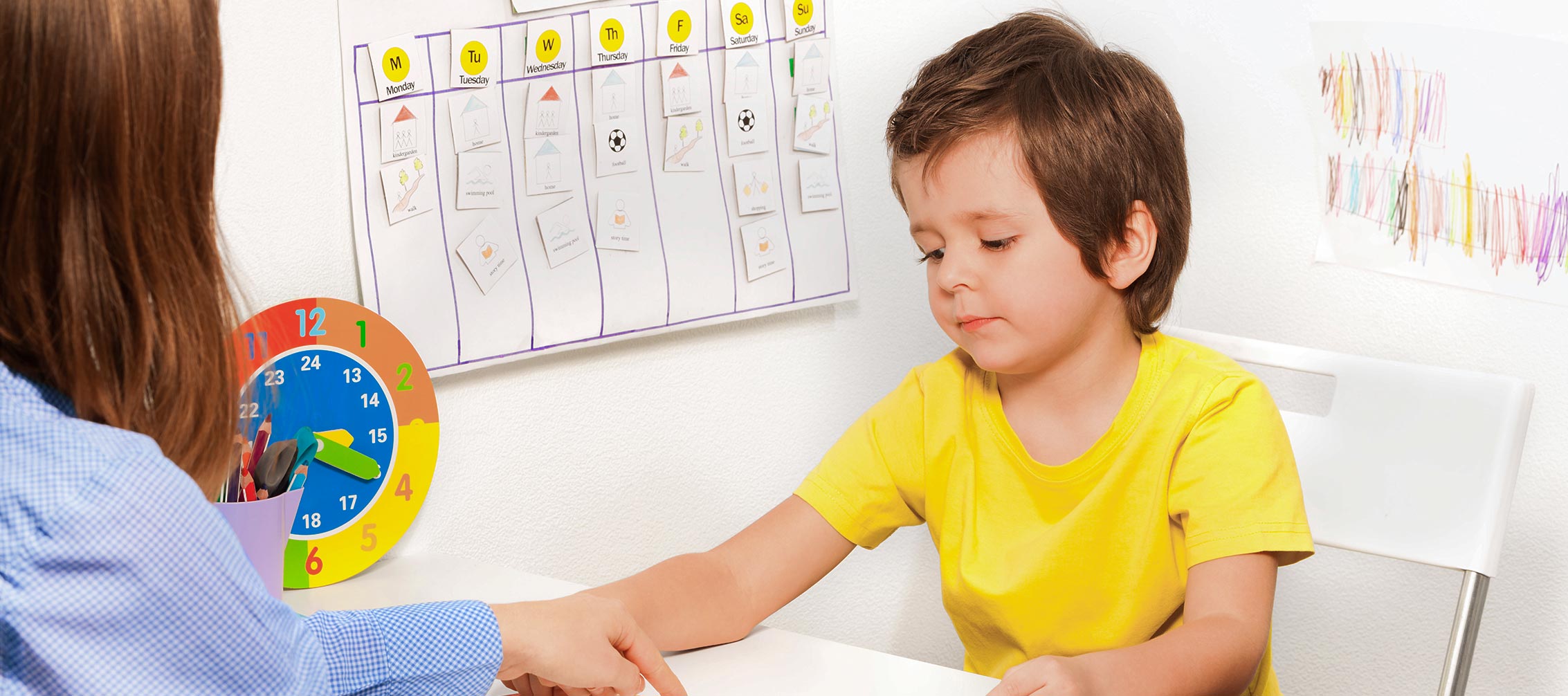
What Happens in an ABA Session?
ABA sessions are structured, personalized, and designed to help children build meaningful skills over time. While each session is tailored to the child’s needs, most follow a consistent format that includes the following core elements:
- Assessment Process
Before therapy begins, a BCBA conducts a thorough assessment to identify the child’s strengths, challenges, and specific goals. This evaluation forms the foundation of the treatment plan. - One-on-One Instruction and Reinforcement
During each session, the therapist works individually with the child using evidence-based techniques. Positive reinforcement is used to encourage learning and reduce behaviors that interfere with progress. - Data Tracking and Family Updates
Therapists collect data throughout the session to measure how the child is responding to the intervention. Families receive regular updates, helping them stay involved and apply the same strategies at home.
What Does ABA Therapy Teach?
ABA therapy helps children build skills that are essential for everyday life. From communication and social interaction to self-care and emotional regulation, the focus is on teaching behaviors that improve independence and overall quality of life.
Focuses on Socially Significant Behaviors
This behavioral intervention targets behaviors that have the biggest impact on a child’s daily life. These are skills that help children engage meaningfully at home, in school, and during social situations.
For example, a child who bites during playtime may be left out of group activities. ABA practitioners address this by teaching more appropriate behaviors—like using words to ask for toys or attention—so the child can join in and connect with others.
Early intervention plays a key role in improving social outcomes. A study in Behavior Analysis in Practice found that 75% of children in ABA programs showed better participation in school and stronger peer relationships. By focusing on socially significant behaviors, ABA helps reduce challenges while building the skills children need to succeed in real-world environments.
Teaches Functional Skills
ABA does more than reduce problem behaviors—it teaches practical skills that help children become more independent and socially connected. For example, if a child screams to get attention, a therapist will teach them to use words, pictures, or gestures instead. Therapists reinforce these new communication tools to help the child use them consistently.
This proactive approach helps children better manage daily routines and social situations. Research published in Autism Research found that over 70% of children who learned alternative skills through ABA showed fewer problem behaviors and stronger communication abilities.
Reinforcement in ABA: Motivation, Not Bribery
Reinforcement is one of the most effective strategies used in ABA therapy. Unlike bribery, which offers a reward in exchange for a behavior, reinforcement encourages positive actions by making them more likely to happen again in the future.
For example, a child might earn extra playtime or a favorite toy after completing a task like cleaning up or following directions. This helps them learn that good behavior leads to positive outcomes.
A study in Behavioral Interventions found that using reinforcement in ABA increased task completion by 60% in children with autism. This structured, motivating approach helps children build meaningful skills—and feel proud of their progress along the way.
ABA in Different Settings
ABA isn’t limited to one location—it can take place at home, in school, or in community settings. This flexibility is important because children learn best when strategies are consistent across their daily environments.
Therapists often work closely with parents, teachers, and caregivers to apply the same techniques in different settings. According to Autism Speaks, ABA therapy has reduced problem behaviors in 88% of cases when applied consistently across environments.
In schools, it helps children manage behaviors that interfere with learning. It supports skills like staying focused, following directions, and interacting appropriately with peers. For instance, instead of calling out, a child might be taught to raise their hand when they want to speak. Therapists and teachers collaborate to make these strategies part of the classroom routine, helping children succeed in academic settings.
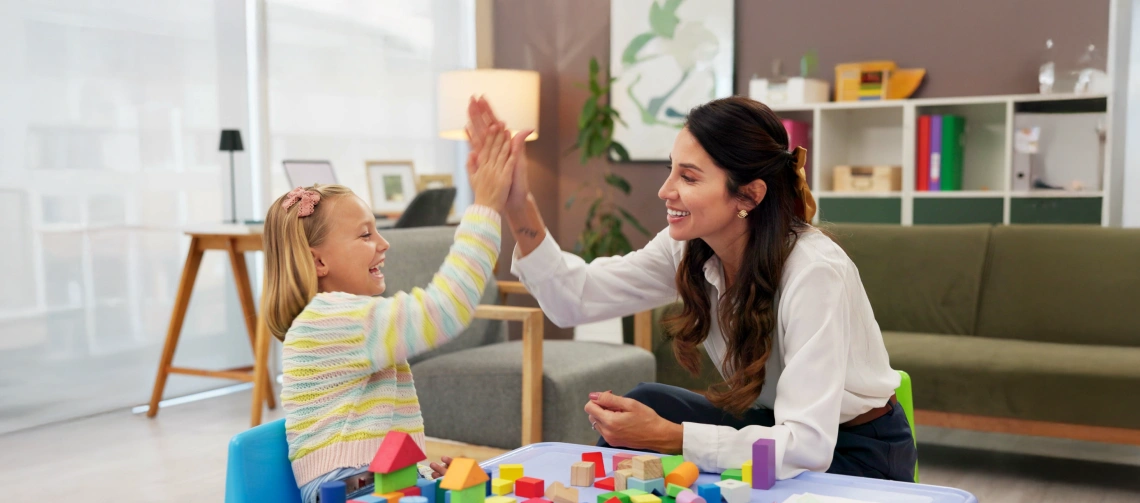
Family Involvement in ABA
Family involvement is a key part of successful behavior support. Parents, siblings, and caregivers are encouraged to participate in the process to help reinforce what the child is learning during sessions.
Research published in the Journal of Child and Family Studies shows that children make more meaningful and lasting progress when their families are actively involved.
Parents are often trained in ABA techniques so they can support their child’s growth at home. By understanding how reinforcement works, they can help their child practice important skills like communication, following directions, and self-regulation. This kind of involvement not only speeds up progress—it also gives families the confidence to support their child’s development every day.
Things You Should Know About ABA
Get the must-know facts about Applied Behavior Analysis—all in one guide
Free downloadBenefits of ABA Therapy
ABA offers a wide range of benefits that help children with autism thrive at home, in school, and in social settings. These improvements often build over time, leading to lasting growth in critical areas of development.
Improved Communication and Social Skills
ABA helps children learn how to express their needs and interact with others more effectively. Whether through spoken words, gestures, or visual aids, improved communication often leads to stronger social connections and fewer behavior challenges.
Greater Independence and Life Skills
Therapists use step-by-step teaching to build essential daily living skills like brushing teeth, getting dressed, or following routines. These skills empower children to take care of themselves and participate more fully in everyday life.
ABA Therapy for a Wide Range of Behaviors
Applied behavior analysis is highly adaptable and can address many different types of behavior. It supports goals such as improving communication, building daily living skills, reducing harmful behaviors, and enhancing social interaction.
One of the most studied areas is its impact on nonverbal children. Research published in Autism Research found that nearly 50% of children receiving ABA therapy developed functional verbal communication skills over time. As children learn to express their needs more clearly, frustration and problem behaviors often decrease.
ABA also helps teach self-care routines like brushing teeth, getting dressed, and eating independently. By breaking these tasks into small, manageable steps, children gain confidence and independence in their daily lives.
Long-Term Benefits of ABA Therapy
The long-term benefits of ABA are well-documented. Not only does it help children develop crucial life skills, but it also prepares them for greater independence as they grow older. A study from the Autism Partnership Foundation found that children who received ABA therapy for at least two years showed a 40% increase in independent living skills by the time they reached adulthood.
Early intervention, particularly before the age of five, is critical for achieving the best outcomes. This evidence-based approach provides the foundational skills that children need to succeed in school, form relationships, and participate in community activities. As they continue to grow and use these skills in new situations, they build the confidence needed for long-term independence.
When and How to Begin ABA Therapy
Starting therapy early can make a meaningful difference in your child’s development. While every child’s journey is unique, research consistently supports the benefits of beginning intervention as soon as possible.
Why Early Intervention Leads to Better Outcomes
Children’s brains develop rapidly in the first few years of life —especially between 18 months and 5 years old. Starting ABA during this critical window helps build key skills—like language, attention, and social interaction—when they’re most likely to stick. The earlier therapy begins, the better the long-term results.
Insurance and Funding Options
ABA therapy is often covered by health insurance, especially when there’s an autism diagnosis. Many states require insurance providers to include ABA as part of autism treatment coverage. In addition to private insurance, families may also qualify for Medicaid programs, early intervention services, or state-funded autism support depending on where they live.
How to Get Started with Mindful Sprouts
If you’re considering ABA therapy for your child, Mindful Sprouts is here to help every step of the way. Our team will guide you through the intake process, answer your questions, and help verify insurance or funding options.
Getting started is simple. Reach out to schedule a consultation, and we’ll work with you to create a personalized plan that fits your child’s unique needs and goals. We’re committed to helping your child thrive—at home, in school, and in life.
Conclusion
ABA therapy offers a scientifically proven, individualized approach to helping children with autism build essential skills and improve socially significant behaviors. Its focus on positive reinforcement, functional skill development, and environmental factors makes it a versatile and powerful tool for promoting long-term success. Early intervention is especially critical, as research shows that starting ABA during a child’s early years leads to the best outcomes. By working closely with children and their families, ABA practitioners help children with autism unlock their full potential, empowering them to thrive in all aspects of life.
Follow us on Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, and Twitter to stay on top of our latest updates.









Leave A Comment